Table of contents
- Node JS
- NVM
- Check your OS
- lsb_release
- Let's get down to business
- Solution
- Open the terminal
- Check the latest NVM versions
- Install NVM
- Make NVM available
- Check NVM installation
- Run nvm
- List available versions
- Install lts Node
- List local Node.js versions
- Set a default version
- Check Node.js default version
- Done
- Celebrate
- Let's become friends
- Final thoughts
Node JS
Node.js is an open-source, cross-platform JavaScript runtime environment that allows developers to execute JavaScript code outside of a web browser.
It is designed for building scalable and high-performance network applications, making it particularly well-suited for building server-side applications and APIs (Application Programming Interfaces).
NVM
NVM is used for managing multiple versions of Node.js on a single machine. It enables developers to switch between different Node.js versions based on project requirements.
NVM is particularly useful when you work on multiple Node.js projects that have specific version dependencies. It ensures that each project can use the appropriate Node.js version without interfering with others.
Check your OS
This step is optional. It's just to make sure you have Fedorainstalled.
/etc/os-release
cat /etc/os-release
hostnamectl
hostnamectl
Output
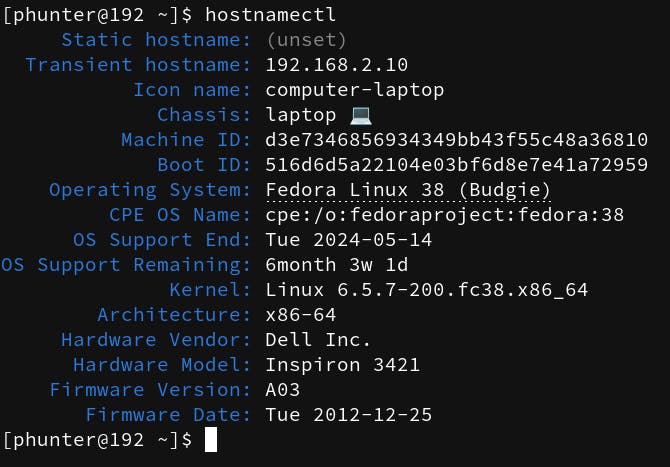
When you run hostnamectl without any options, it provides detailed information about the system's hostname, operating system, kernel, and other system-related settings.
lsb_release
lsb_release -a
Output
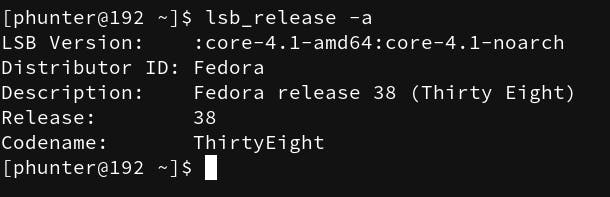
lsb_release is a command-line utility commonly found in Linux distributions that adhere to the Linux Standard Base (LSB). The LSB is a standardization initiative that aims to increase compatibility between different Linux distributions by defining a common set of libraries and conventions.
uname
uname -a
Output

The uname -a command is used to display detailed system information about the Linux operating system. It provides information about the system's kernel and other system-related details.
Let's get down to business
shall we?

Solution
Open the terminal
Check the latest NVM versions
Go to the releases page and write down the last version.
At the moment, the link is:
https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm/releases
Install NVM
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.5/install.sh | bash
Replace v0.39.5 with the chosen version.
Output
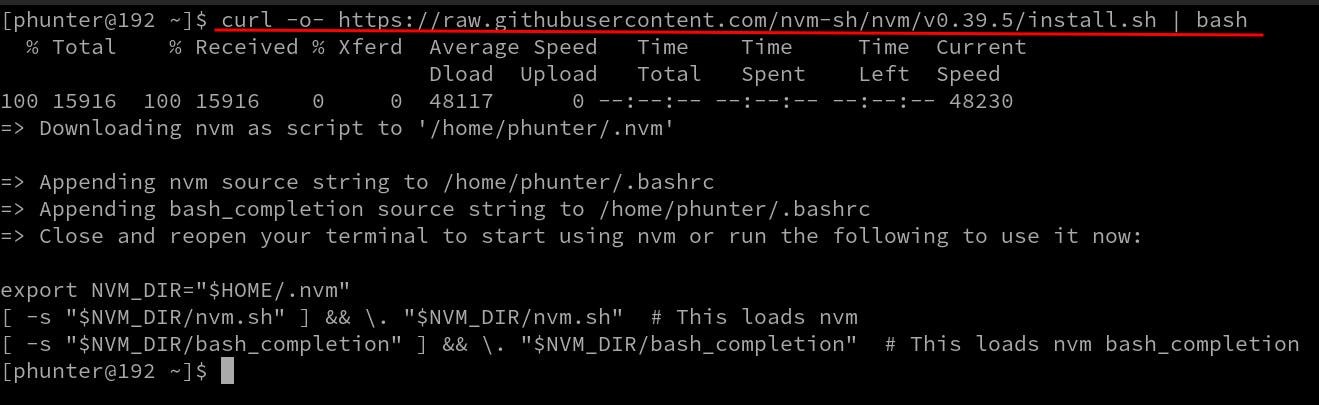
curl is the command-line tool for making HTTP requests.
It can be used to download files, make API requests, and perform various other HTTP-related tasks.
-o is a flag that is used to specify the output file for the downloaded content. By default, curl will save the downloaded content to a file with a name derived from the URL.
When you use -o followed by a filename, it tells curl to save the content to that specific file.
The catch is that when you use -o- (with a hyphen after it), it instructs curl to send the output to stdout instead of saving it to a file.
Make NVM available
source ~/.bashrc
The command source ~/.bashrc is used to execute the content of the .bashrc file in the current shell session. It is commonly used in Unix-like operating systems, including Linux, to apply changes made to the configuration file without the need to log out or start a new terminal session.
When you run source ~/.bashrc, you are telling your current shell session to read and execute the commands in your .bashrc file. This is often done to apply changes to environment variables, aliases, functions, or other shell settings that you've modified or added to your .bashrc file.
Check NVM installation
Version
nvm --version
Executable file's path
which nvm
Run nvm
nvm
List available versions
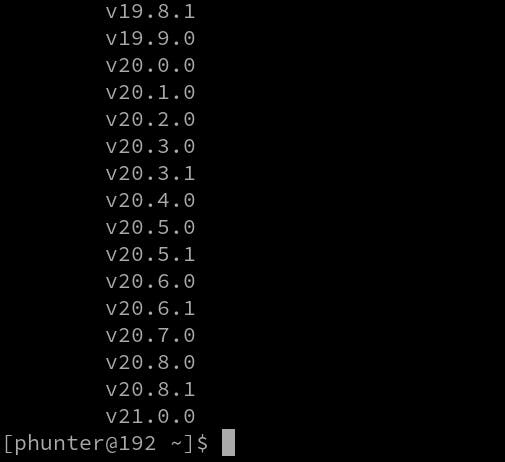
nvm ls-remote
Output
Install lts Node
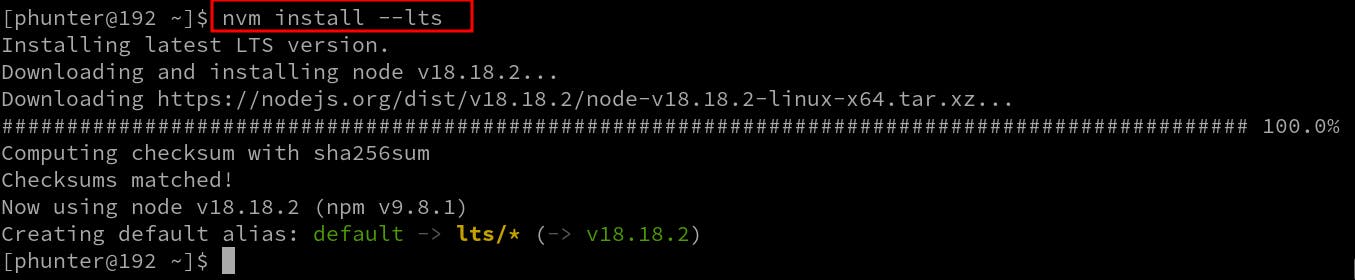
nvm install --lts
Output
List local Node.js versions
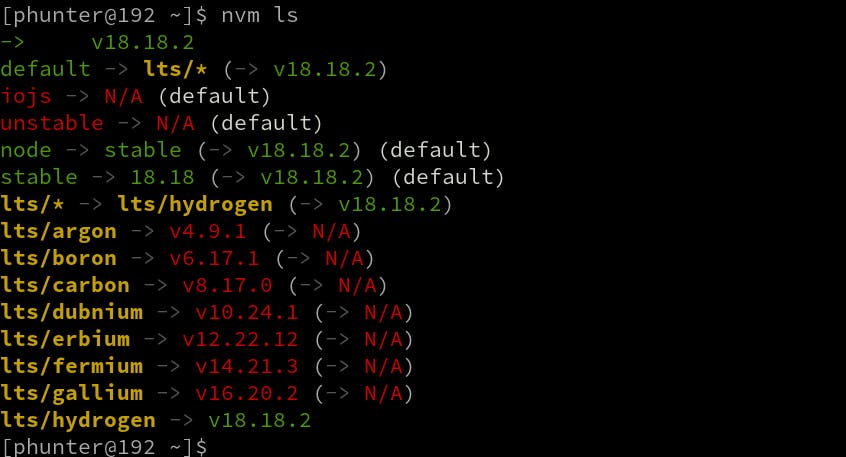
nvm ls
Output
Set a default version
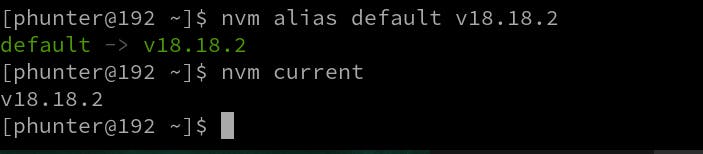
nvm alias default v18.18.2
Output
Check Node.js default version
nvm current
Output
Done
Celebrate

Let's become friends
Final thoughts
Thank you for reading this article.
If you have any questions, thoughts, suggestions, or corrections, please share them with us.
We appreciate your feedback and look forward to hearing from you.
Feel free to suggest topics for future blog articles. Until next time!

