Docker
Docker is a platform for developing, shipping, and running applications in containers.
Containers are lightweight, portable, and self-sufficient units that can package an application and its dependencies, including libraries and configuration files, into a single, consistent environment.
This allows developers to create, deploy, and manage applications more efficiently, regardless of the underlying infrastructure.
Let's get down to business
Shall we?

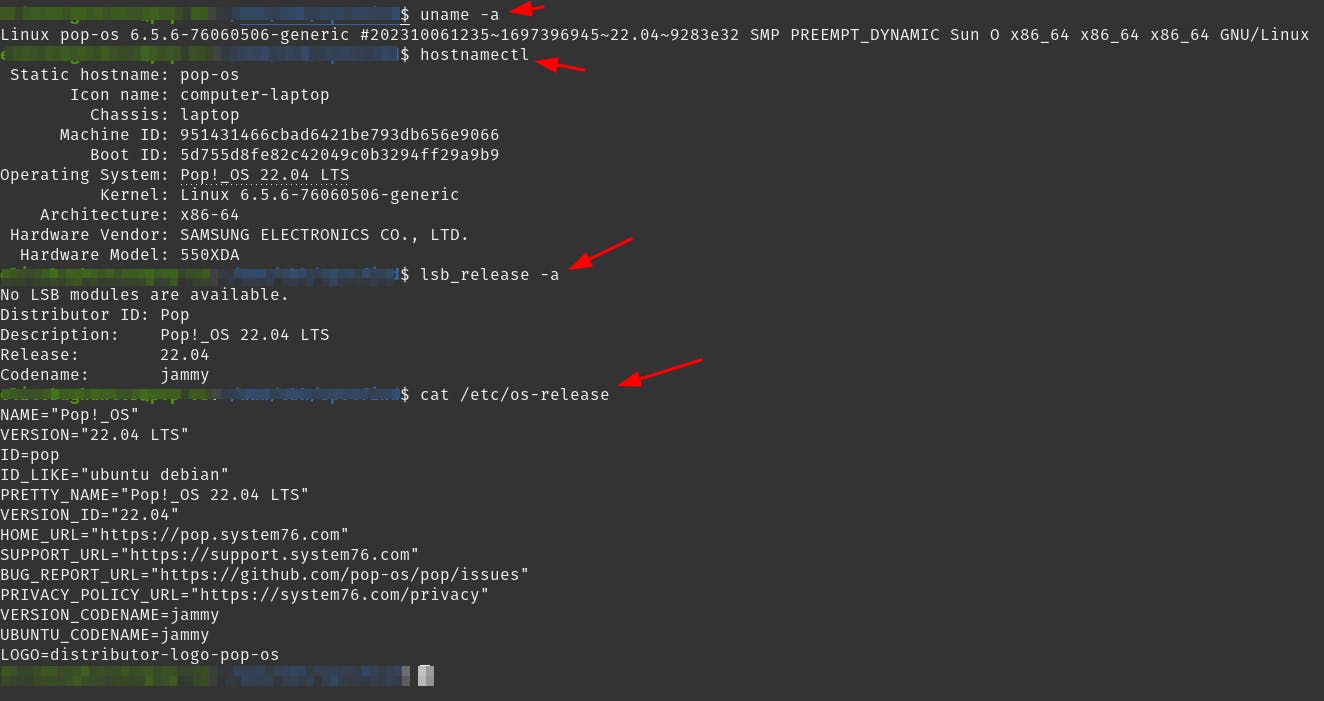
Check your OS (optional)
This step is just to make sure you have Pop!_OS installed.
uname -a
hostnamectl
lsb_release -a
cat /etc/os-release
Output
Open a Terminal
Update packages info
sudo apt-get update
Running sudo apt-get update is an important step before installing or upgrading packages on your system because it ensures that you have the most up-to-date information about available packages.
Without updating the package index, you might not see the latest versions of software or be able to install new packages that have been added to the repositories since the last update.
Install dependencies
sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl gnupg
Set up a directory for keyrings
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
Output

The command you provided is creating a directory with specific permissions for apt keyrings.
Keyrings are used in package management systems, like APT (Advanced Package Tool) in Debian-based systems, to manage cryptographic keys for package verification.
Download Docker GPG
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
Output

The command you've provided is using curl to download the Docker GPG (GNU Privacy Guard) key from the specified URL and then using gpg to convert it into a format suitable for APT package management
Change permissions
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
Output

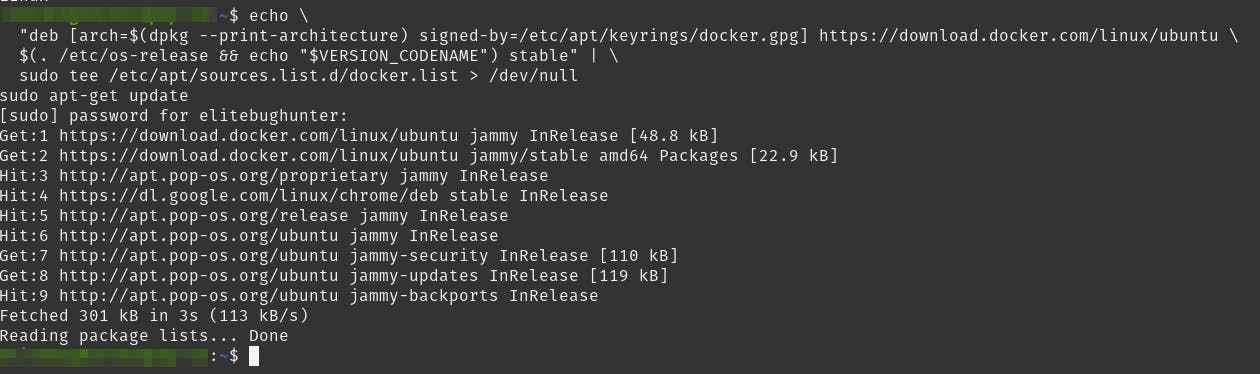
Add the repository
echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME") stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
Output
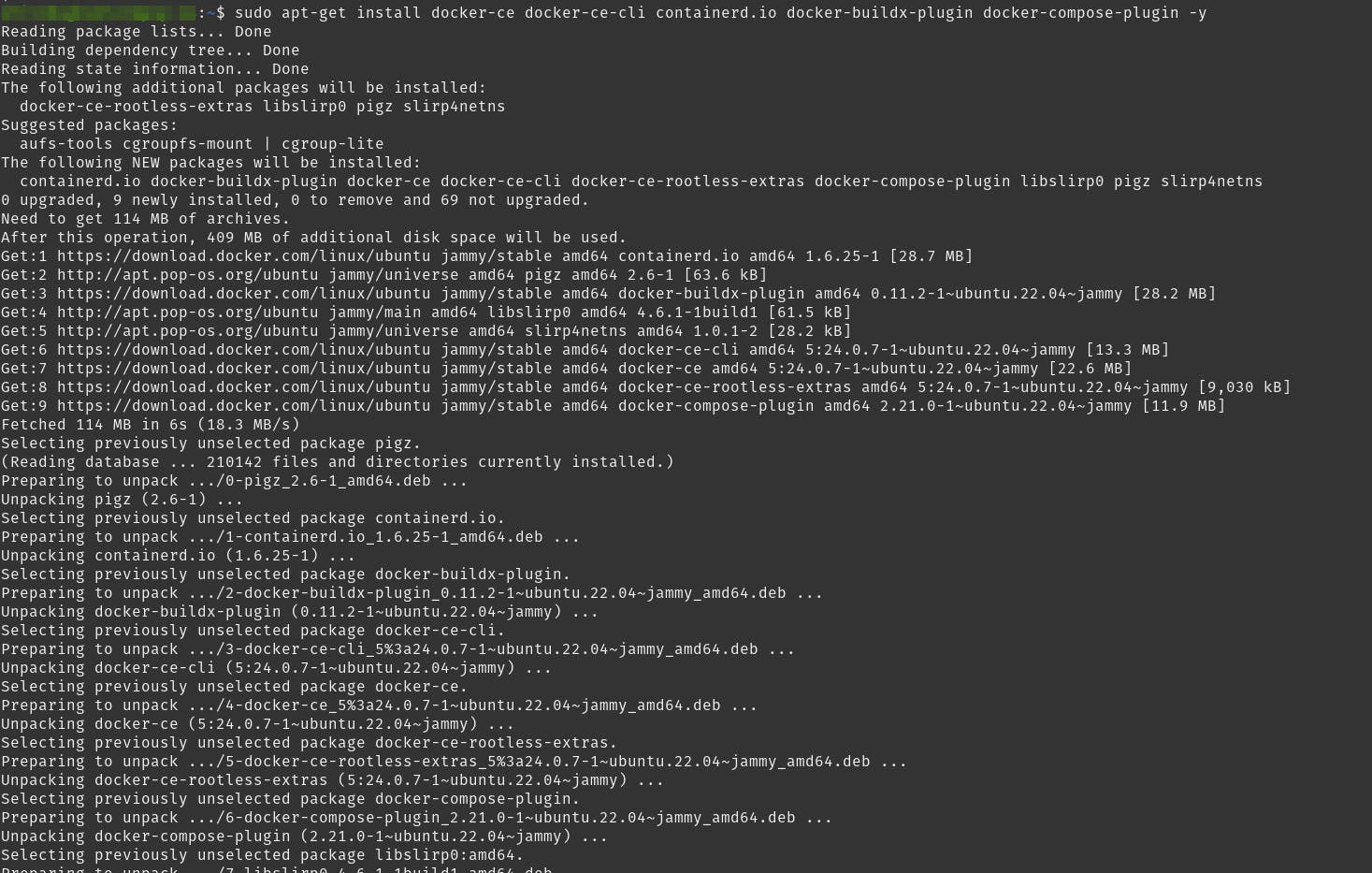
Install the Docker packages
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin -y
Output
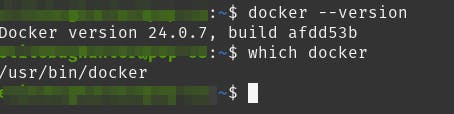
Confirm installation
docker --version
which docker
Output
Run Docker
Let's verify that the Docker Engine installation is successful by running the hello-world image.
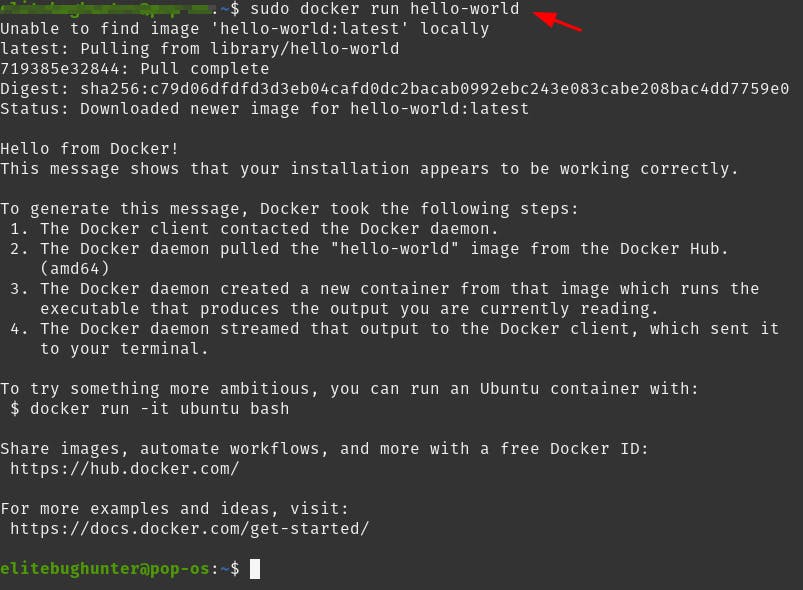
Done
Celebrate

Let's network
Final thoughts
Thank you for reading this article.
If you have any questions, thoughts, suggestions, or corrections, please share them with us.
We appreciate your feedback and look forward to hearing from you.
Feel free to suggest topics for future blog articles. Until next time!


