Photo by Rubaitul Azad on Unsplash
How to install Docker on Elementary OS 6.1 or any other Ubuntu-based Linux distribution via the terminal emulator?
Table of contents
Check your operating system
LSB release
lsb_release -a
Output
lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Elementary
Description: elementary OS 6.1 Jólnir
Release: 6.1
Codename: jolnir
The lsb_release -a command is used to display detailed information about the Linux distribution on your system.
It stands for "Linux Standard Base release" and provides information such as the distribution's name, release number, codename, and more
Linux installed
cat /etc/os-release
Output
cat /etc/os-release
NAME="elementary OS"
VERSION="6.1 Jólnir"
ID=elementary
ID_LIKE=ubuntu
PRETTY_NAME="elementary OS 6.1 Jólnir"
LOGO=distributor-logo
VERSION_ID="6.1"
HOME_URL="https://elementary.io/"
DOCUMENTATION_URL="https://elementary.io/docs/learning-the-basics"
SUPPORT_URL="https://elementary.io/support"
BUG_REPORT_URL="https://github.com/elementary/triage/issues/new"
PRIVACY_POLICY_URL="https://elementary.io/privacy-policy"
VERSION_CODENAME=jolnir
UBUNTU_CODENAME=focal
The cat /etc/os-release command in the terminal will display the contents of the /etc/os-release file, which contains information about the Linux distribution installed on your system.
if it's Ubuntu-based, you might see something in ID_LIKE,UBUNTU_CODENAME or another attribute.
Update packages info
sudo apt-get update
Running sudo apt-get update is an important step before installing or upgrading packages on your system because it ensures that you have the most up-to-date information about available packages.
Without updating the package index, you might not see the latest versions of software or be able to install new packages that have been added to the repositories since the last update.
Install required dependencies
sudo apt install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
In summary, the provided command is used to install essential packages and utilities that are commonly required for adding external repositories, securely fetching packages over HTTPS, and managing software sources on an Ubuntu system. These packages are often necessary for setting up and maintaining software on your system.
Add Docker GPG key
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
Output

Add the Docker repository to the apt sources list
sudo add-apt-repository \
"deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu bionic stable"
The command constructs a repository source entry for Docker, based on your distribution's codename (obtained using lsb_release -cs), and then writes that entry to the /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list file.
This is how you add a Docker repository source to your APT configuration on a Debian-based system, ensuring that APT can find and install Docker packages from the specified repository.
Update package info
sudo apt-get update
Install docker
sudo apt-get install docker-ce
then
sudo apt-get install docker-ce-cli containerd.io
Output
Check installation
Through version
docker --version
Output

Through executable path
which docker
Output

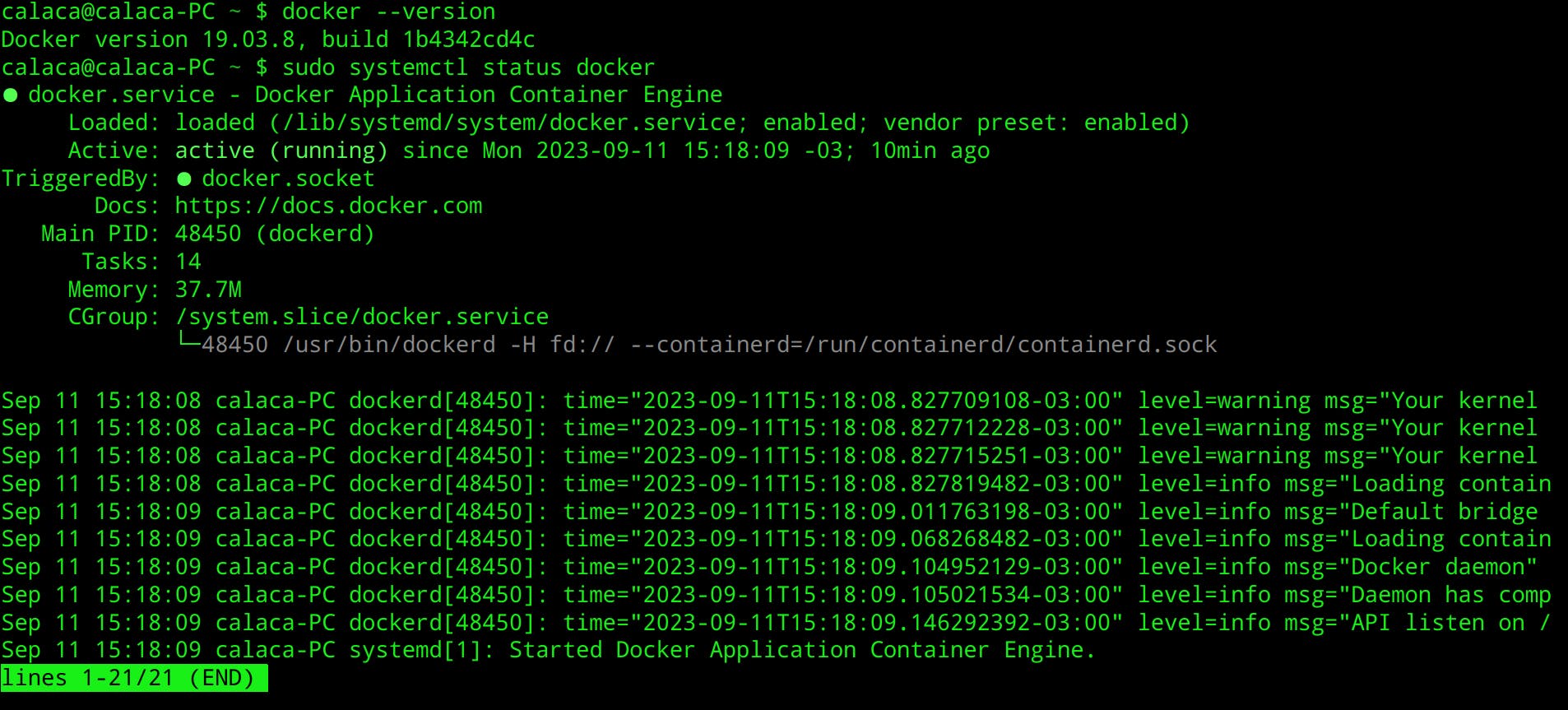
Check status
sudo systemctl status docker
Output
Restart the Operating System
Test
sudo docker run hello-world
Done
Celebrate
You've made it!

Let's become friends
Final thoughts
I hope this article has been helpful to you. Please feel free to reach out if you have any questions. Your thoughts, suggestions, and corrections are more than welcome.
By the way, don't hesitate to drop your suggestions for new blog articles.
I look forward to seeing you next time.

