Debian
Debian is a popular and influential open-source operating system known for its stability, security, and commitment to free and open-source software principles.
It serves as the foundation for various other Linux distributions, including Ubuntu and many others.
Debian has a rich history and has been influential in shaping the landscape of the Linux and open-source software world. Its commitment to stability, security, and open source makes it a trusted choice for server deployments, development environments, and personal desktops.
Debian-based distribution
Knowing if your operating system is Debian-based is crucial for efficient system management and software compatibility.
Understanding your OS's heritage can lead to smoother updates, troubleshooting, and adherence to Debian's security advisories.
Moreover, it helps you navigate the Linux community and access relevant documentation and support channels.
Different Linux distributions have specific resources and forums tailored to their users. Being part of the Debian-based community ensures you receive guidance and support aligned with your system's configuration and practices.
Methods
Each operating system has its unique configuration, and that's why we offer multiple methods to help identify whether your OS is Debian-based.
1-LSB Release
lsb_release -a
Possible output
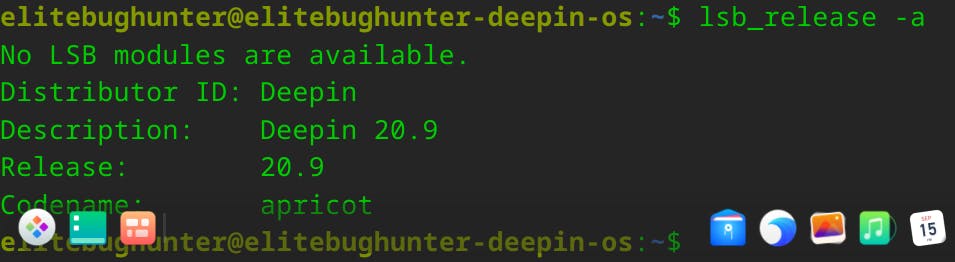
The lsb_release -a command is used to display detailed information about the Linux distribution on your system.
It stands for "Linux Standard Base release" and provides information such as the distribution's name, release number, codename, and more.
2-Linux installed
cat /etc/os-release
Possible output:
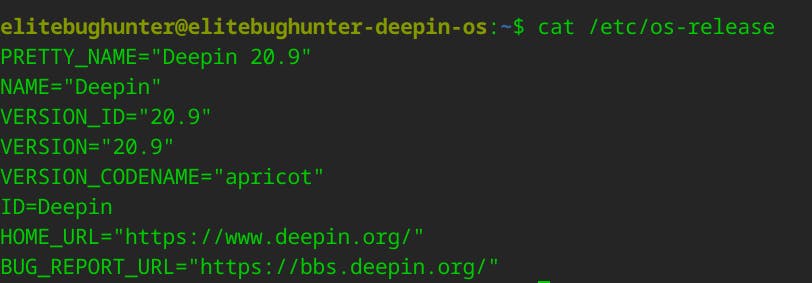
The cat /etc/os-release command in the terminal will display the contents of the /etc/os-release file, which contains information about the Linux distribution installed on your system.
if it's Debian-based, you might see something in ID_LIKE,UBUNTU_CODENAME or another attribute.
3-Kernel version
uname -r
Possible output:
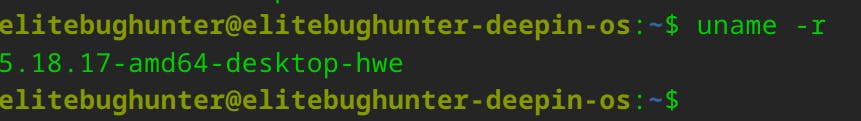
When you run uname -r in a terminal, it will output a string that represents the kernel version.
This information can be useful for various purposes, such as checking the kernel version for compatibility with certain software or drivers, troubleshooting system issues, or simply gaining a better understanding of your system's configuration.
4-Display Debian version
cat /etc/debian_version
Possible output:
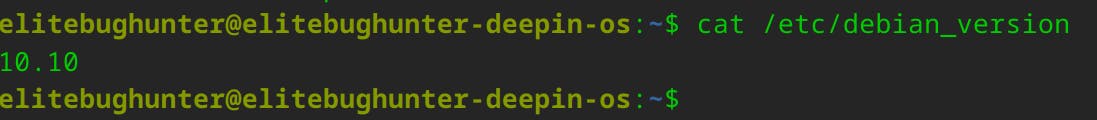
The cat /etc/debian_version command is used in Debian-based Linux distributions to display the specific version of the Debian operating system that is installed on your system.
This information can the version of Debian installed on your system, especially when you need to determine compatibility with software or when seeking support for Debian-related issues.
5-Check package managers
dpkg --version
Possible output:
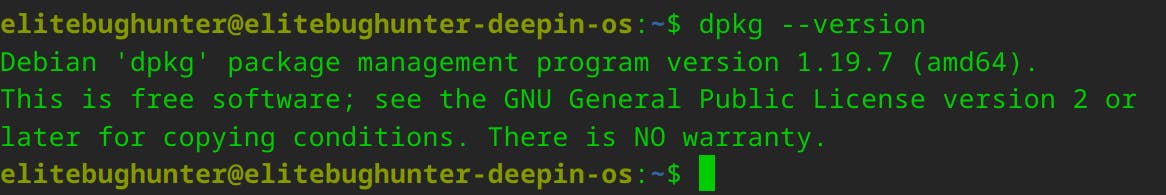
The dpkg --version command is used to display the version of the Debian package management system (dpkg) that is installed on your Linux system.
When you run this command in the terminal, it will provide information about the dpkg version installed.
6-Check repositorires source
ls /etc/apt/sources.list.d/
If you see files with names related to Debian or its derivatives (e.g., "ubuntu.list" for Ubuntu), it's an indication that the system is Debian-based.
7-Inxi command-line utility tool
inxi is a versatile command-line tool that provides extensive system information, making it useful for system administrators, troubleshooting, or simply gaining insights into your system's setup.
8-Neofetch command-line utility tool
neofetch provides information about your operating system, kernel version, CPU, GPU, memory usage, and more.
It also allows for customization through command-line options or configuration files to change the ASCII art or include additional details.
Done
Celebrate
You've made it!

Let's become friends
Final thoughts
I hope this article has been helpful to you. Please feel free to reach out if you have any questions. Your thoughts, suggestions, and corrections are more than welcome.
By the way, don't hesitate to drop your suggestions for new blog articles.
I look forward to seeing you next time.

