Photo by Artiom Vallat on Unsplash
Quick and Easy Way to Check Your Linux Installed System's RAM Memory
Greeting
Hey guys, how've you been? It's AC, Alexandre Calaça here. I'm so excited that you landed here. Hope you enjoy this new article.
By the way, I would be glad to receive your feedback about this one and other articles.
Introduction
This article Quick and Easy Way to Check Your Linux Installed System's RAM Memory is going to show how
Check your OS
lsb_release -a
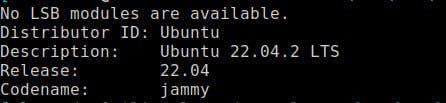
If you have Ubuntu, you'll end up with something like this
If you have another distribution, such as Deepin Os. You'll see something like this:

The LSB command
The lsb_release -a command is used to display certain LSB (Linux Standard Base) and distribution-specific information about the Linux distribution you are running.
It prints the following information:
Distributor ID
Description
Release
Codename
This command is available on most modern Linux distributions that use the LSB. However, some smaller or less mainstream distributions may not have the command installed by default. In that case, you may need to install the lsb-release package to get access to the lsb_release command.In programming, a collection refers to a data structure that stores a group of related elements. Collections are used to organize and manage data in a way that makes it easy to access and manipulate.
Verify your installed RAM
Open the terminal and run the following command:
sudo dmidecode --type 17
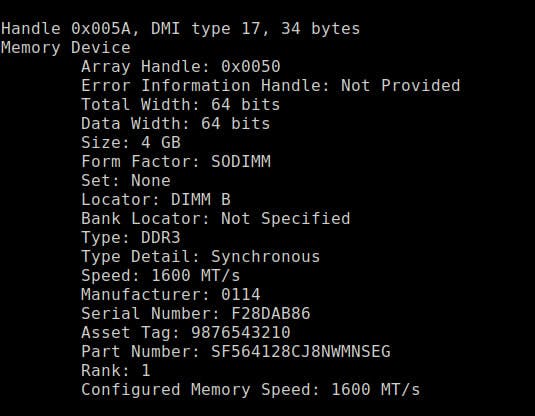
On Ubuntu, you'll see something like this

On Deepin Os, you'll see something like this

dmidecode command
The sudo dmidecode --type 17 command is a Linux command used to display information about memory devices installed on a computer system.
Specifically, it uses the dmidecode tool to retrieve the System Memory Array information, which includes details about the maximum capacity, type, and number of memory slots available on the system.
The dmidecode tool reads the system's DMI, which stands for Desktop Management Interface data, which is a standardized way to describe a computer's hardware components, such as the motherboard, BIOS, and peripherals.
By specifying --type 17, the command filters the output to only show information about the memory devices. The output includes details such as the manufacturer, part number, serial number, size, speed, and type of memory modules installed on the system.
Summary
In this article, we learned how to use the dmidecode command. dmi stands for Desktop Management Interface data.
We used the --type 17 argument, by using it, it output only information about the memory devices.
Celebrate
If you read the article, kudos! you did a great job. You can celebrate for sure!

Conclusion
That's all for today. Thanks for reading the article Quick and Easy Way to Check Your Linux Installed System's RAM Memory.
I hope this article helped you. Let me know if you have any questions.
Your thoughts, suggestions and corrections are more than welcome.
By the way, feel free to drop your suggestions on new blog articles.
Hope to see you next time.